Industry Analysis
Global dating app market expanded at 12% CAGR between 2019-2024 and was valued at $6.2b, while global dating app users expanded at 4% CAGR to 365M over the same period. Yet, growth rate varies significantly among countries in the most recent year. E.g. US experienced no growth in 2024 v.s. global market grew by 18% in 2024. The growth in global dating app market was primarily driven by outperformance in China and India, fueled by population growth, urbanization, and rising mobile users.
The global market is highly fragmented, and dominant players vary by region. Bumble held approximately a 14% market share in terms of global dating app market revenue in 2024. Tinder, the leading app, captured 16%. Hinge, captured 4%. The top 3 dating apps collectively accounted for just 34% of the global market, suggesting that no single app possesses a dominant competitive advantage on a global basis and that the market remains highly competitive and fragmented.
The market structure in the U.S. is high concentrated. Tinder app and Bumble app together dominates the market with 49% market share in 2024. In addition, the top five apps made up more than 80% of the market, suggesting a highly concentrated market.
The key markets that Bumble App operates in are expected to grow slower than the overall market growth. Yet, the networking effect makes it extremely difficult for Bumble app to expand to high growth regions such as Asia Pacific as there are already dominant players in the region.
Succeeding in a market dominated by a leading player often requires a mix of innovation and fortunate timing. Bumble's app achieved notable success in the U.S. due to three key factors: (1) introducing a unique niche feature that empowers women to initiate conversations, (2) capitalizing on user dissatisfaction with Tinder—such as its high prevalence of bots—as the market leader with over 40% share, and (3) entering during a period of rapid market growth exceeding 10% annually, which lowered barriers to entry.
Competing in the U.S. dating app industry remains extremely challenging. Over the years, Bumble and Hinge emerged as the only two players able to significantly expand their combined market share, rising from 2018 to 2024. During this period, Tinder's share declined from 43% to 29%. Meanwhile, the combined share of all other players dropped sharply from 37% to 12%. This shift underscores the ongoing consolidation in the market, driven by economies of scale and the need for substantial resources among leading platforms like Tinder, Bumble, and Hinge. Across the U.S. and other key markets where Bumble operates, this trend highlights the critical role of scale, network effects, and operational efficiency in achieving long-term success in the dating app industry.
Executive Summary
Bumble operates as a franchise business that dominates multiple regional dating-app markets by leveraging powerful network effects and economies of scale. Growth rate and market structure in dating app industry varies significantly among regions. Long-term success increasingly requires scale, network effects, and operational efficiency, making it extremely challenging to compete against established players without exceptional timing, innovation, and favorable market conditions. As such, ongoing market consolidation is likely to continue in saturated markets.
BMBL’s high return on invested capital (excluding goodwill and intangible assets) underscores the strength of its underlying business operations. However, when goodwill and intangible assets are included, ROA falls markedly, suggesting that management has yet to fully translate that operational strength into shareholders’ returns.
With the founder’s return, Bumble has announced a renewed emphasis on quality. Although it remains uncertain whether these initiatives will reignite growth, they should reinforce the company’s leadership in its established markets.
Suggested entry price of $5. Current price of $6.5 offers insufficient downside protection despite the fact that the business itself is capable of generating strong cash returns in the short to mid-term. I would not consider buying at current levels.
Value Proposition
The ultimate goal of dating apps is to monetize through subscriptions and in-app purchases in a carte menu. Users are willing to pay for premium features that enhance their experience, such as advanced filters, unlimited swipes, or boosted visibility. Users experience would be a function of (1) number of real users, (2) quality of matches and (3) product innovation. Within the U.S., Bumble App has expanded its market share in terms of MAUs, yet ARPPU and paying users continue to fall in the most recent quarters highlights the decreasing ability to monetarize from its users.
Historically, Bumble app was sidetracked to business and friendship where it had no competitive advantages and as a result, has not been successful. In 2017, the time it introduced its business platform, LinkedIn already had a total of 491m users. Networking effect has kept users from using Bumble Bizz. On friendship platform Bumble BFF, it had only 1 million active users as of 1Q25. Past acquisitions have not been successful. BMBL has decided to pause two (Fruitz and Official) out of the three acquisitions. This is expected to be completed by 1H25.
Past attempts to improve customer experience did not result in a turnaround. BMBL relaunched its Bumble App in 2Q24 with a new marketing campaign showcasing a refreshed brand identity and new product features. New product features include AI-powered tools to enhance profile creation and fake account detections with refreshes to the Bumble Premium+ tier. Bumble app also attempted to introduce new subscriptions tiers such as Premium+. None of this was able to turn its US business around.
Looking forward, Whitney Wolfe Herd, who stepped down as Bumble CEO in November 2023 and returned to the CEO role in mid-March 2025, mentioned the priority is to improve the quality of the platform as opposed to increasing users / international expansion. This would be achieved through
(a) Improving the member base by modernizing the personalized matching algorithm with AI and enhanced machine learning to promote and elevate quality Bumble members to better enable those relevant matches.
(b) Aggressive cost cutting that would save $40M OPEX a year to invest in product innovation and
(c) Reduced marketing budget by $20M for 2Q25 in order to improve the user base.
The new initiatives would assure Bumble app dominance in its already saturated market. Whether these could result in restoring growth is hard to tell as the previous attempt on rebranding has proven unsuccessful. On another hand, allocating cost towards product innovation is better than on OPEX.
Expansion to a new market with dominant players require very specific conditions. Its expansion in high growth countries will not be as smooth as the way it expanded in the US since it has to compete with large regional players.
Business Moats
Networking effects and economies of scale effectively bar smaller competitors from entering Bumble’s core markets, ensuring that larger players remain dominant, as illustrated by the market-share analysis above. Moreover, the company’s high return on invested capital (excluding goodwill and intangible assets) underscores the strength of its underlying business operations. However, when goodwill and intangible assets are included, ROA falls markedly, suggesting that management has yet to fully translate that operational strength into shareholders’ returns.
Networking effects are prominent in BMBL’s key markets, making it increasingly difficult for smaller players and new entrants to gain traction against established platforms with larger user bases.
Economies of scale further strengthen BMBL’s position. By spreading fixed costs across its two platforms, the company can allocate more resources to research, development, and marketing, as demonstrated by the U.S. market’s consolidation over the past five years. Together, these dynamics effectively block smaller competitors from entering Bumble’s core markets, ensuring that larger players continue to dominate.
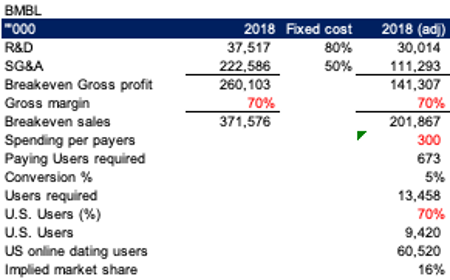
Getting a sense on the moat. For the business to be viable, the business would require ~670k payers to cover 80% R&D and 50% SG&A expense of what BMBL spent in 2018 when it first started. Assuming 70% of the users are from the U.S., the new players would need about 16% market share of the total U.S. online dating users just to breakeven. Historically, only two players (BMBL and MTCH) were able to achieve this scale within the U.S. market. In our opinion, this is a highly sustainable barrier of entry.
The historical ROIC (excluding goodwill and intangibles) and adjusted operating margins of BMBL highlights the presence of business moats. Operating margins has been above 20% majority of the quarters and return on invested capital has always been above the cost of capital. However, when goodwill and intangible assets are included, ROA falls markedly, suggesting that management has yet to fully translate that operational strength into shareholders’ returns.
Asset value
Dating app industry of BMBL’s key markets are likely to remain viable in the foreseeable future. As such, reproduction asset value is likely more relevant than the liquidation value.
Significant assets on book are Goodwill and Intangible assets. Both figures may not represent any economic value and have been set at zero value.
Intangibles – Revenue base is based on 2x CAC per payers between 2022-2023 * total number of payers. The use of 2022 and 2023 CAC should represent the costs to acquire new payers under a normalized market environment. We doubled the CAC to reflect the difficulties to acquire customers from scratch.
Intangibles – Portfolio Product represents 1.5 year of R&D GAAP (excluding restructuring costs) expenses. Looking at how Bumble App was started, Whitney Herd founded Bumble shortly (~3months) after leaving Tinder in 2014. The short launching time was partially attributable to her experience in the dating app industry. To take a prudence approach, we estimated the R&D costs to reproduce similar app to be 1.5 year of R&D GAAP expenses.
Intangibles – Trained labor force simply represents ~2 years of G&A (GAAP less restructuring costs) expenses.
Note: The equity value is irrelevant due to high liabilities.
Earnings Power Value
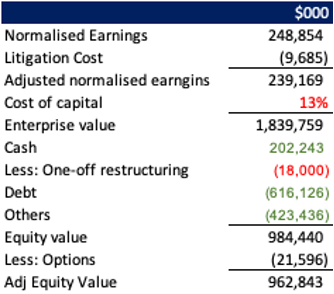
Operating earnings were adjusted to better reflect the underlying economics of the business. Annual litigation cost was estimated based on historical average. CAPEX has been minimal and has been consistently below the depreciation expenses. On stock-based compensation specifically, the portion was added back to the operating earnings, but the option value was deduced from the enterprise value.
Bumble’s earnings power value substantially exceeds its asset reproduction value, highlighting the company’s strong competitive advantages. For a platform like Bumble, it is more appropriate to use enterprise value as the basis for valuation, as traditional asset-based approaches understate the value of its network effects and brand strength.
Valuing the Franchise Business
Component 1: Cash return
Market cap of BMBL as of 12 July 2025 is $670m and debt amounted to $620m. Including the outstanding options, acquiring the business would require $1.5b.
Assuming BMBL will reinvest 30% of its future $40M savings and to estimate 80% of the annualized 1Q25 revenue is sustainable, the estimated sustainable distributable cash amounted to $240m per year, or 16% cash return.
Component 2 – Organic growth
Depends heavily on overall users’ growth, innovation and less on inflation.
Referencing to data released by Statista in Dec 2023. The number of users of online dating in the U.S. between 2023-2028 is estimated to expand at a CAGR of 2.2%. For simplicity, assume the growth rate is similar in all key markets.
Given Bumble App regional dominant position and points discussed, its market share within the key markets will at least remain stable in the long term.
The most recent price increases for its subscription service were in Aug 2021, meaning the revenue is unlikely to correlate with inflation.
To be conservative, the total return from organic growth would be 2.2%. Based on the historical working capital requirement, for every $1 increase in profits would need to be funded by $0.3 working capital. This leaves a net return of 1.5%. We attribute no growth to international expansion in high growth regions.
Component 3 – Active investments
Management’s historical attempts to accelerate growth include (1) acquisitions and (2) expanding the platform beyond dating to friendship and business. None of this were considered successful.
Given the historical poor capital allocation, we assume the management adds no value to the return.
Component 4 – Franchise Fade
On one hand, the barrier of entry is highly sustainable. On the other hand, the dating app industry is subject to technology disruption or changes in consumers behavior due to low switching cost. Using the half-life business method, a 10-year half-life corresponds to an annual fade rate of 7.2%. (72/10)
Putting the numbers together
Total return of 11% (16%+2.2%-7.2%). Given that the business is highly leveraged, the cost of capital would be around 12%, buying the business at the current price represents very little margin of safety. Suggested entry would be $5.
Disclaimer: This blog is a personal documentation of my own investing journey, thoughts, and experiences. It is intended solely for self-documentary purposes and general informational sharing. It does not constitute investment advice, financial recommendations, or personalized guidance. By reading this blog, you acknowledge that you are responsible for your own financial decisions and that the author assumes no liability for any actions taken based on the content herein.